RF Phase Shifter Buying Guide
Precisely adjust the phase angle of RF signals without compromising quality or impedance matching. Control phase relationships between signals with accuracy using an RF phase shifter.
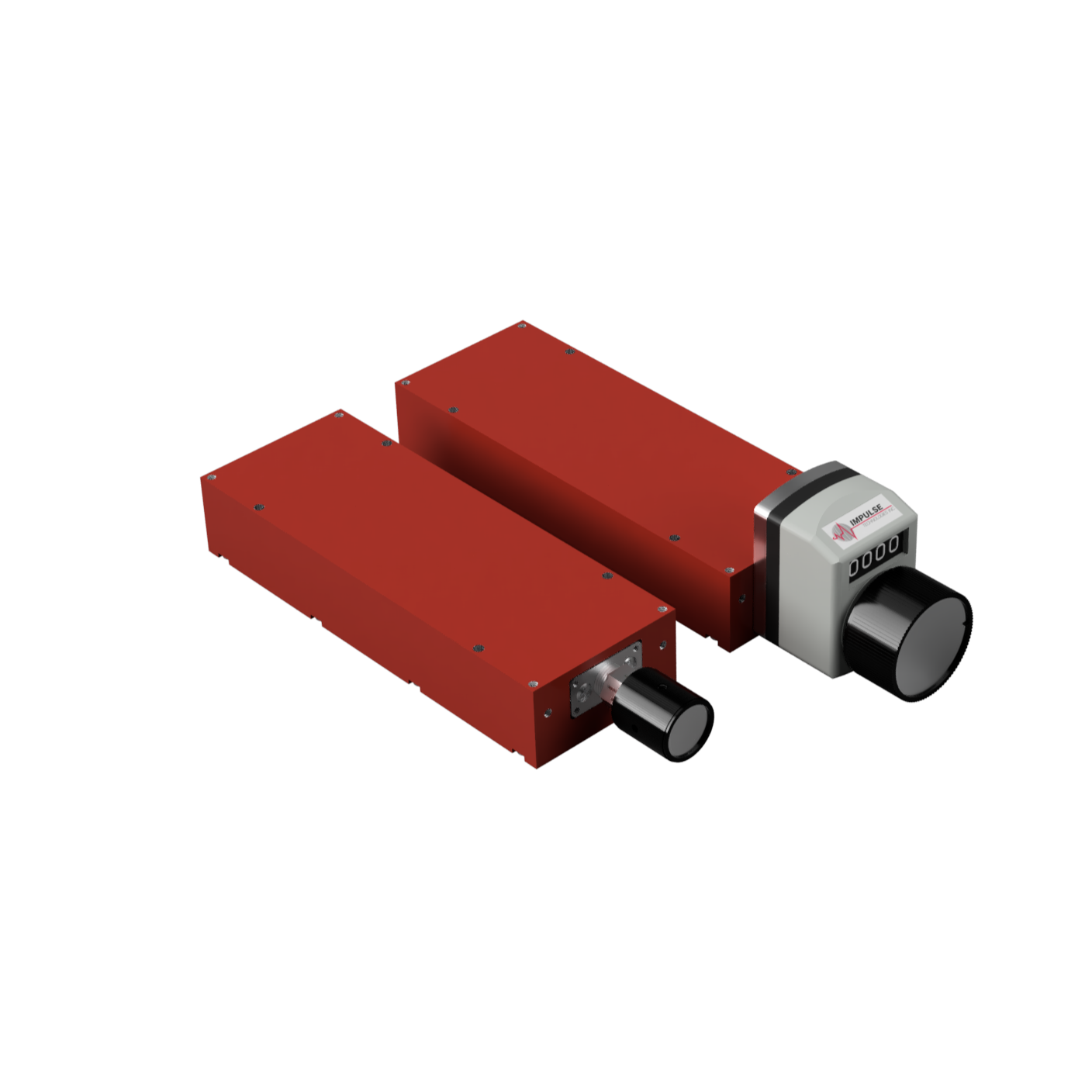
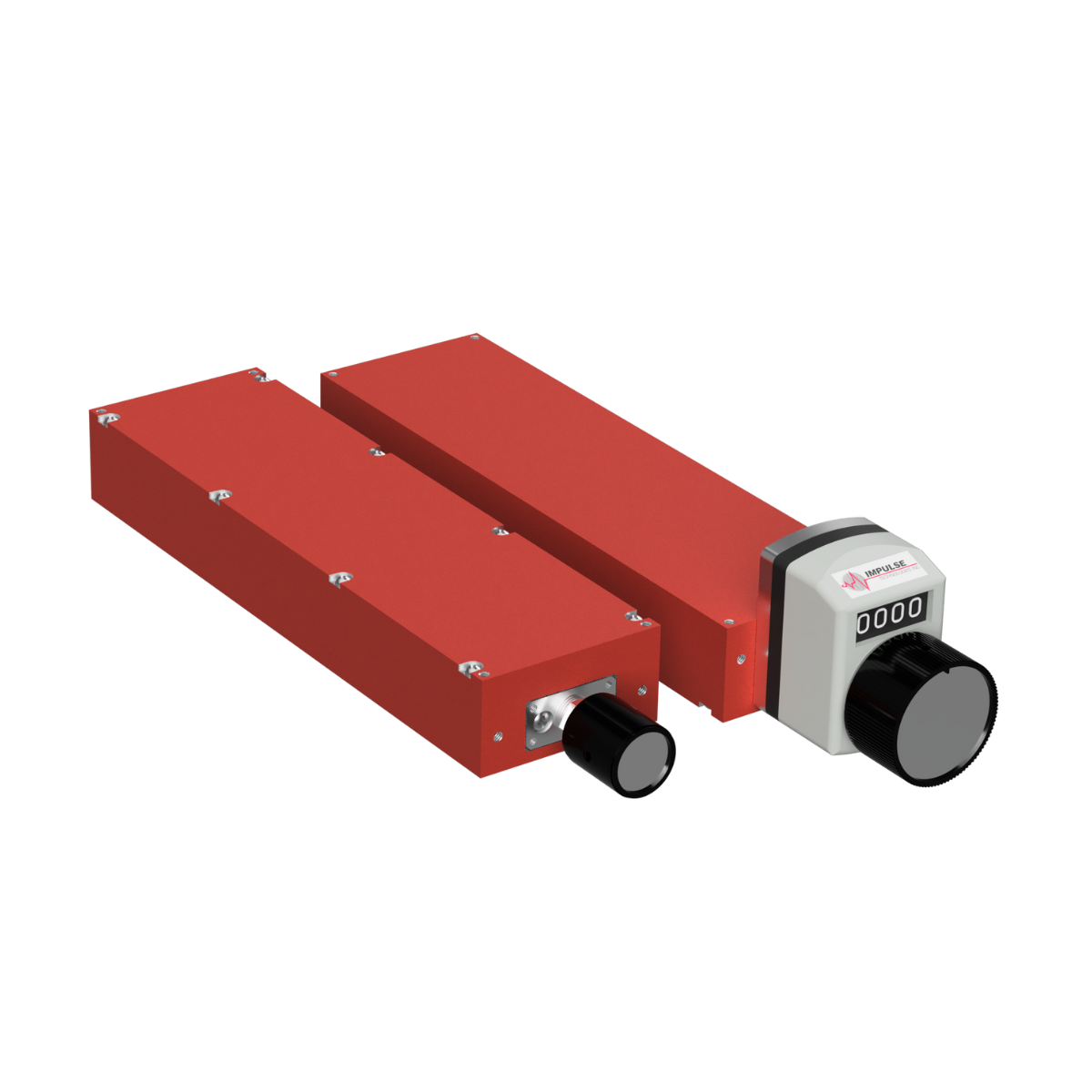
Impulse Technologies manufactures three mechanical phase shifter series - 30°, 60° and 90° — each with a range of models to fit various production testing and signal control applications.
What to Look for in an RF Phase Shifter
When comparing phase shifters, pay attention to these features:
How to Choose the Right Type of RF Phase Shifter
Whether your RF design process requires precise phase control or the ability to function at specific frequency bands, Impulse Technologies has a model that matches your needs.
Mechanical Phase Shifters
Mechanical phase shifters are controlled manually with a knob or digital dial. You can adjust the phase from input to output by turning the knob, allowing for precise control.
These phase shifters offer higher power handling capabilities, lower VSWR, and lower insertion loss compared to other types. While they may be larger than digital or analog alternatives, they provide exceptional reliability and performance for lab environments and testing applications.
Bottom Line:
Choose mechanical phase shifters for laboratory testing, calibration setups, and applications requiring manual precision adjustment with minimal signal degradation.
Digital Phase Shifters
Digital phase shifters are programmable and can be controlled via a computer interface. They provide discrete phase states and exhibit fast switching speeds with flat phase performance over the defined frequency range.
While they typically have higher VSWR and insertion loss than mechanical phase shifters, they excel in automated test environments and systems requiring remote control.
Bottom Line:
Choose digital phase shifters for automated test systems, remote applications, and scenarios requiring consistent, repeatable phase shifts.
Analog Phase Shifters
Analog phase shifters are controlled by a voltage level, with phase shift changes based on the applied control voltage. These provide continuously variable phase adjustment for very precise phase setting.
These analog devices generally have lower insertion loss than digital models. However, phase performance may vary across the frequency range — unlike digital models that maintain flat phase response.
Bottom Line:
Choose analog phase shifters for applications requiring fine continuous phase adjustment and systems with voltage-controlled interfaces.
What to Know About Impulse Technologies' Phase Shifter Series
Impulse Technologies produces three mechanical phase shifter series to meet different testing and development needs.
30° Phase Shifters
Our 30° Phase Shifters are designed for applications requiring moderate phase adjustment with high precision at higher frequencies up to 40GHz. These models feature continuous adjustment throughout a 30° per GHz phase range and low insertion loss for maximum signal integrity. This series offers a choice of standard knob or digital counting dial.
60° Phase Shifters
Our 60° Phase Shifters are manufactured for applications requiring a wider range of phase adjustment, particularly at lower frequencies, while maintaining excellent performance. These models feature continuous adjustment throughout a 60° per GHz phase range, low insertion loss, and standard 50 Ohm impedance. The series offers a choice of standard knob or digital readout.
90° Phase Shifters
Our 90° Phase Shifters are manufactured for applications requiring a wider range of phase adjustment while maintaining excellent performance. These models feature continuous adjustment throughout a 90° per GHz phase range, low insertion loss, and standard 50 Ohm impedance. Frequency ranges as low as 4GHz achieve 360° min. The series offers a choice of standard knob or digital readout.
How Long Do Phase Shifters Last?
When procuring RF phase shifters, it's important to budget for their lifecycle. These factors affect the average lifespan of a phase shifter:
-
Mechanical Components
Last 5 to 10 years with standard use. The mechanical component (i.e., the knob) is the most common breaking point, as it can wear out with consistent use.
-
Connectors
Can degrade after repeated mating cycles. Using proper torque specifications when connecting can significantly extend their lifespan.
Test and calibrate phase shifters regularly to confirm they still match the system's operational demands and perform within specifications, regardless of age.
RF Phase Shifter Pricing
Pricing for these devices depends on several factors, including:

Model Type
Different types of phase shifters (mechanical, digital, or analog) have different price points based on their design complexity and capabilities. Mechanical phase shifters typically cost less than digital models due to their simpler construction, while analog models generally fall between the two.

Frequency Range
Models with wider bandwidth or specialized frequency bands may have a higher price point due to the precision engineering required.

Lead Time
Urgency also plays a part in phase shifter pricing. In-stock standard items typically have a lower price point than those we produce to special requirements.

Quantity
Single items generally have a higher unit price. We offer bulk pricing for 10+ items.
Additional components to be considered
- Cables with SMA or Type-N connectors that fit the device's ports
- Cable assemblies with sets of phase-matched pairs
- Adapters to pair the device with existing equipment
- Power meters to monitor and confirm signal characteristics
- RF amplifiers and power amplifiers for signal enhancement
- Mixers and combiners for signal processing
- Attenuators for signal level control
- Directional couplers for signal sampling
- Waveguide components for high-frequency applications
- Bias tees for DC power insertion
- Terminations for unused ports
Why Choose Impulse Technologies for RF Phase Shifters?
With over 30 years of experience in the industry, Impulse Technologies verifies each unit against rigorous performance standards before shipment from our Bay Shore, New York headquarters.
In addition to phase shifters, we offer complete signal control solutions — including variable RF attenuators, waveguide to coaxial adapters, and standard gain horn antennas — all designed to work together seamlessly in your RF systems.
Our ISO 9001:2015-certified processes ensure consistency from unit to unit, with comprehensive documentation to support your quality requirements. For specialized applications, our engineering team can design custom phase shifters with specific frequency ranges, control mechanisms, or connector types to address your exact needs.

FAQs About RF Phase Shifters
-
RF phase shifters are frequently used in RF systems where precise control of signal phase is required. Common applications include phased array antennas for radar and communication systems, RF testing and measurement equipment, signal processing systems, and beam steering applications. They're also essential components in transceivers and converters for telecommunications.
-
Phase shifters typically fit into one of these categories:
- Mechanical Phase Shifters: Use physical adjustments to change signal phase
- Digital Phase Shifters: Provide discrete phase states controlled electronically
- Analog Phase Shifters: Use control voltage for continuous phase variation
- Fixed Phase Shifters: Deliver a consistent phase shift
- Solid-State Phase Shifters: Use semiconductor technology like GaAs for phase control
Mechanical phase shifters offer advantages in precision, reliability, and low insertion loss. For more advanced functionality, MMIC-based phase shifters provide compact solutions for surface mount applications.
-
RF phase shifters operate by physically adjusting the length of the transmission path that the RF signal travels through. This adjustment uses precision components such as line stretchers that lengthen or shorten the signal path. Impulse Technologies' digital dial provides phase change readings at 1 GHz, which can be scaled up to the frequency of interest by multiplying by that frequency in GHz.
-
Key specifications include:
- Phase range (measured in degrees per GHz)
- Frequency range (measured in GHz or MHz)
- Insertion loss (measured in dB)
- VSWR (measured as a ratio)
- Power handling capacity (measured in W or dBm)
- Impedance (typically 50 Ohms)
- Amplitude variation across the operating bandwidth
-
Consider these important factors:
- Required phase range (30° vs 60° vs 90° per GHz)
- Frequency range and bandwidth of your application
- Power levels in your system
- Required precision of phase adjustment
- Physical space available for installation
- Whether you need additional components like splitters, isolators, or circulators
- Whether manual adjustment or digital readout is preferred
Impulse Technologies can help match your requirements to the optimal phase shifter model.
-
Phase shifters work with various RF components including:
- Attenuators and limiters for amplitude control
- Power dividers and hybrid couplers for signal distribution
- Amplifiers to compensate for insertion loss
- Oscillators and synthesizers in frequency generation systems
- Modulators for signal processing
- Equalizers for frequency response compensation
Proper impedance matching between components ensures optimal system performance.